The National Sports Governance Act, 2025, is a landmark law that fundamentally reforms how sports are managed in India.
It has improved existing rules and regulations for all sports organizations in the country. It mandates strict, legally enforceable rules for all national sports organizations, replacing the previous, informal guidelines.
This article helps you understand the details of the National Sports Governance Act, 2025. Read on to understand the Act’s impact on Indian sports, its crucial role in safeguarding athletes, and why this legislative change was essential.
Below, we outline the significant changes introduced by this new law.
Summary Of The National Sports Governance Act
The National Sports Governance Act is a complete law that creates new obligations and improves existing ones in order to manage Indian Sports in an improved manner.
Here is a simplified overview of the National Sports Governance Act 2025:
| Key Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| The Law | Sports governance in India now follows binding legal rules, not just guidelines. |
| Who It Covers | NOC, NPC, National Sports Federations, Regional Federations. |
| New Bodies | National Sports Board (oversight) and National Sports Tribunal (disputes) |
| Fair Elections | Election Panel with retired officials ensures transparent sports body elections. |
| Athlete Safety | Safe Sports Policy to protect athletes from abuse/harassment. |
| Transparency | Code of Ethics + RTI coverage make sports bodies more accountable. |
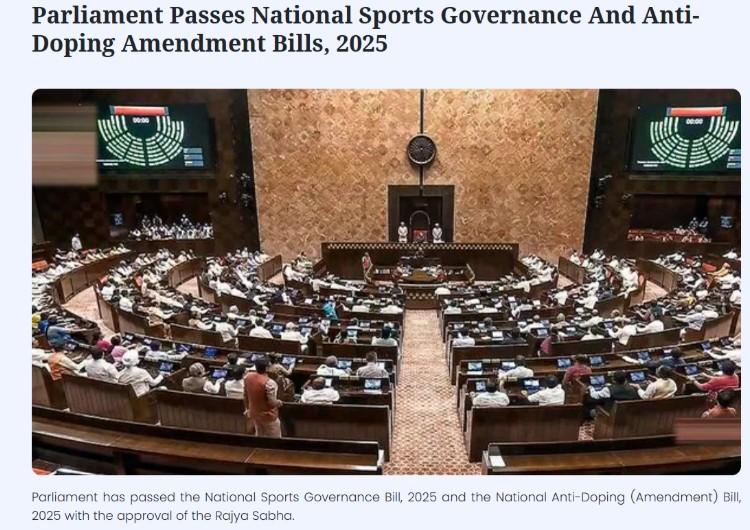
Parliament has passed The National Sports Governance Act 2025 and Anti-Doping Amendment Bill on 12th August, 2025. The bill was introduced in Lok Sabha on July 23, 2025.
It solves problems such as a lack of transparency and weak athlete protection. The expected results include cleaner elections in sports bodies, better ways to solve disputes, and stronger safety measures for athletes.
This law covers all major sports bodies in India, including the National Olympic Committee (NOC), National Paralympic Committee (NPC), National Sports Federations, and Regional Federations.

The Act creates two important new bodies: The National Sports Board and the National Sports Tribunal.
The Act introduces professional election management through an Election Panel made up of retired election officials.

It also requires a Safe Sports Policy to protect athletes. The Act creates a Code of Ethics for all sports bodies and brings sports organizations under the Right to Information (RTI) Act. This means these organizations must be more open about their work.
5 Key Objectives of the National Sports Governance Act, 2025
The Act has five main goals that will change Indian sports management and create a better environment for athletes and sports development.
1. Promote the Development and Welfare of Sportspersons
The Act puts athletes at the center of sports management. It makes sure that every National Sports Body must have athlete representation in its Executive Committee.
This leads to athletes having a direct voice in decisions that affect their careers and well-being. The law also creates specific ways to address athlete concerns and complaints quickly.
2. Ensure Transparency and Accountability in Sports Bodies
Sports organizations must now work like public bodies when it comes to being open. The Act brings all recognized sports bodies under the RTI Act.
This brings transparency to sports management. They must publish audited financial accounts and follow strict financial reporting rules. This openness helps prevent misuse of public money and corruption.
3. Establish Unified Governance Framework Across All National Sports Bodies
Before this Act, different sports bodies followed different rules and structures. Now, every National Sports Body must have the same basic structure.
They need a General Body, Executive Committee, Ethics Committee, Dispute Resolution Committee, and Athletes Committee. This standard setup makes it easier to watch and make sure all sports have good management.
4. Align Indian Sports Governance with Olympic and Paralympic Charters
The Act ensures that Indian sports bodies comply with international standards set by the Olympic and Paralympic movements. This alignment is crucial for maintaining India’s participation in international competitions.
The law specifically requires that all national bodies follow the International Charters and Statutes while adapting to Indian legal needs. This will improve Olympic sports involvement in national sports to a large extent.
5. Facilitate Effective Dispute Resolution Mechanisms for Sports-Related Grievances
The creation of the National Sports Tribunal provides a specialized forum for resolving sports disputes quickly.
Instead of time-consuming court battles, sports-related conflicts with some exceptions can now be resolved by experts who are knowledgeable in sports law and governance. This speeds up justice delivery and reduces disruption to sports activities.
National Sports Governance Act: Structural Reforms and Governance Provisions
The Act introduces required structural changes that every recognized sports body must implement to ensure they have better management and representation.
| Committee | Composition | Key Roles | Special Provisions |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Body | Equal representatives from all levels | Overall governance and policy formulation | Includes ex officio and affiliate members |
| Executive Committee | Up to 15 members maximum | Day-to-day administration | Minimum 2 athletes, 4 women required |
| Ethics Committee | Appointed expert members | Enforce Code of Ethics and conduct | Special focus on protecting vulnerable groups |
| Grievance Redressal | Internal committee structure | Resolve complaints timely and transparently | Direct access for athletes, coaches |
| National Sports Board | Government-established oversight body | Grant/suspend recognition, oversee compliance | Works with international sports bodies |
These structural changes ensure that sports bodies operate democratically with proper representation. The Ethics Committee and Grievance Redressal mechanisms provide safeguards against misconduct and abuse.
The requirement for minimum athlete and women’s representation addresses the historical exclusion of these groups from sports governance.
All the changes can also positively impact Indian Sports Infrastructure, leading to more development.
Athlete Protection and Welfare Measures in the National Sports Governance Act
The Act introduces several steps specifically designed to protect athletes and improve their well-being within the sports system.
1. Safe Sports Policy
Every National Sports Body must implement a comprehensive Safe Sports Policy that focuses on preventing abuse, harassment, and misconduct, especially against women and minors.

This policy covers physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, creating clear guidelines for safe training environments. The policy also establishes protocols for reporting and investigating complaints while protecting the identity of complainants.
2. Grievance Mechanisms
The Act mandates that all recognized sports bodies establish internal grievance redressal mechanisms accessible to athletes, coaches, and associated persons.
These mechanisms must ensure fairness, maintain strict timelines for resolution, and provide multiple channels for filing complaints. Athletes can approach these committees directly without fear of retaliation.
3. Athlete Representation in Governance
For the first time in Indian sports law, the Act guarantees athlete representation in governance structures. Every Executive Committee must include at least two athletes.

There must be a separate Athletes Committee. This ensures that athlete voices are heard in policy decisions and that their concerns receive proper attention from sports administrators.
4. Alignment with Anti-Doping Rules
The Act works alongside existing anti-doping legislation to ensure that athlete welfare includes protection from performance-enhancing drugs.

It establishes clear procedures for handling doping-related issues while maintaining the integrity of sports competitions and protecting clean athletes.
National Sports Governance Act Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
The National Sports Tribunal addresses the long-standing problem of delayed justice in sports disputes.
The Tribunal consists of:
- A Chairperson, who must be a current or former Supreme Court Judge or High Court Chief Justice.
- Two expert members with knowledge of sports, law, and administration.
This composition ensures both judicial expertise and sports-specific understanding.
The Tribunal has jurisdiction over most sports disputes but excludes certain matters.
- It cannot hear cases during major international events to avoid disrupting competitions.
- Matters that fall under the exclusive jurisdiction of internal dispute committees
- Doping disputes covered by the National Anti-Doping Act
- Matters requiring resolution through international forums like the Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS).
The Tribunal operates with civil court powers, meaning it can summon witnesses, require document production, and receive evidence. Its orders are executable as civil court decrees, making them immediately enforceable.
Appeals from Tribunal decisions go directly to the Supreme Court, except where international rules specify alternative forums.
This system provides speedy, specialized resolution of sports disputes while maintaining respect for international arbitration requirements.
It reduces the burden on regular courts and ensures that sports disputes are resolved by people who understand the unique nature of sports governance.
Source: National Sports Governance Act,2025
Challenges and Critiques of the National Sports Governance Act
The main worry is about the balance between government control and sports body freedom.
- Sports federations fear that the National Sports Board’s wide powers, including suspending recognition and appointing temporary administrators, may interfere with their independence.
- International sports bodies, especially the IOC, have always opposed government interference in sports management.
- The Tribunal’s limited jurisdiction presents another challenge. By excluding matters during international events and following international arbitration rules, the Tribunal’s effectiveness may be reduced.
- The Act creates many duties for sports bodies, but monitoring mechanisms may be weak.
- Compared to IOC and FIFA models, India’s approach seems more government-focused, which may create tensions with international requirements for independent governance.
Why Was a Sports Governance Act Necessary in India?
The sports system and the major sports policies in India had some loopholes that hurt sports development and athletes interests.
Problems in the old system:
- Sports bodies followed the 2011 Sports Code which were just guidelines, not laws
- Federations could ignore rules without any punishment
- Poor management structures in most sports bodies
- No transparency in financial matters
- Athletes were not included in the decision making process
Key reasons reforms were needed:
- The same officials stayed in power for decades through rigged elections
- Public funds were misused without proper accountability
- Athletes faced harassment with no complaint system
- Very few women in leadership positions
- Each federation worked differently – no standard rules
- Court cases took years, disrupting sports and athlete careers
How the Act solves these problems:
- Creates legal rules that must be followed
- Requires open financial reporting
- Guarantees athlete and women representation
- Sets up professional election management
- Provides specialized dispute resolution
- Implements complete athlete protection measures
Conclusion: The National Sports Governance Act, 2025, Improves Indian Sports Management!
By creating legal frameworks for transparency, accountability, and athlete welfare, the Act addresses decades of poor governance in Indian sports bodies.
The Act balances government oversight with sports autonomy by involving international bodies in key decisions. Its focus on athlete protection through Safe Sports Policies shows a commitment to creating safer sports environments.
However, success depends on proper implementation. The National Sports Board, Election Panel, and Sports Tribunal must work effectively. All stakeholders must collaborate to make this Act work successfully.
FAQs
The National Sports Governance Act, 2025, creates a legal framework for managing sports organizations in India, replacing the previous system of voluntary guidelines.
The Act protects athletes through mandatory Safe Sports Policies to prevent abuse and harassment, guaranteed representation in governance bodies, accessible grievance redressal systems, and specialized dispute resolution through the National Sports Tribunal.
Key reforms include standardized structures for all sports bodies, mandatory athlete and women’s representation, election management through retired election officials, transparent financial reporting, and oversight by the National Sports Board.
The National Sports Tribunal is a specialized judicial body that resolves sports disputes quickly and efficiently. Headed by a senior judge with expert members, it has civil court powers, and its orders are directly enforceable.
The Act mandates consultation with international bodies for key decisions and defers to international arbitration where required, ensuring India maintains its participation in global sports competitions.